Understanding and Using Technical Indicators in Market Research and Analysis
Technical indicators, a crucial aspect of market research and analysis, are mathematical calculations that use historic market data such as price, volume, and open interest to predict future market trends. They bestow traders with visually accessible insights into the market trends and potential trading opportunities. This piece delves into an in-depth understanding of how technical indicators work and how to use them in market research and analysis.
Types of Technical Indicators
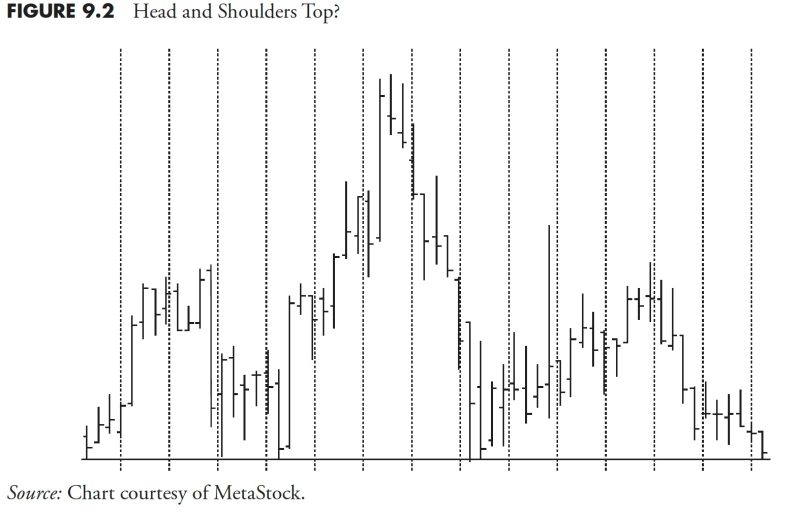
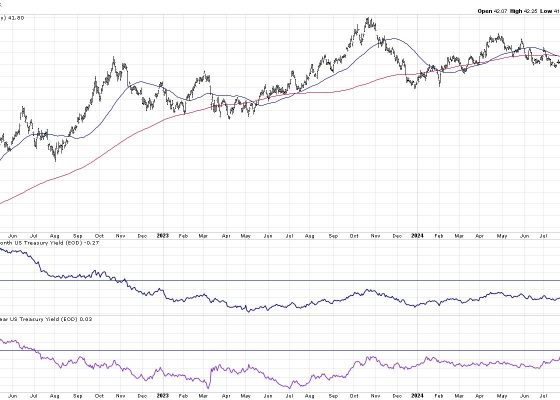
There are four main types of technical indicators that each yield unique and invaluable insights into market behavior. The first group is trend indicators, such as moving averages, which help identify market trends and spots when those trends potentially change. Next are momentum indicators such as the Relative Strength Index (RSI), which measure the speed of price movements. Volatility indicators, like Bollinger Bands, measure the magnitude of price fluctuations, aiding traders in understanding the level of market uncertainty. Finally, volume indicators showcase the number of shares or contracts traded within a specific time frame, providing insights into the strength or weakness of a trend.
Using Technical Indicators in Decision Making
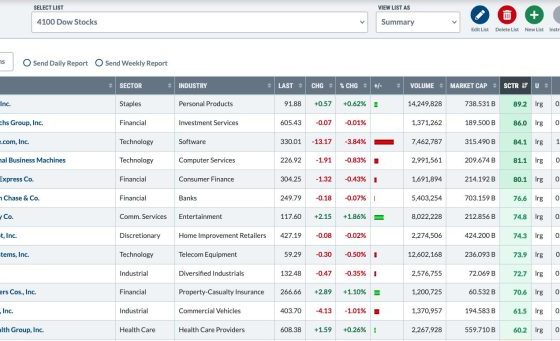
Technical indicators can grant valuable market signals, helping traders make a plethora of decisions. For instance, a trader might use momentum indicators to determine when to buy or sell an asset. Suppose when RSI exceeds 70 (overbought territory), the trader might decide to sell, predicting the price will descend as the market corrects. Volatility indicators can help traders make decisions on risk management, indicating when to tighten or widen stop losses based on market fluctuations. Volume indicators can double-check the credibility of the other indicators, indicating the strength of a trend, thereby providing confirmation to enter or exit a trade.
Drawing Conclusions from Multiple Indicators
By incorporating multiple indicators into their analysis, traders can formulate a comprehensive perspective of market behavior. Each indicator yields different insights, and using multiple indicators together can provide confirmation of market trends and signals. This technique, termed ‘confirmation’, assists traders in engineering more reliable strategies. For example, a trader might use both a trend indicator and a momentum indicator to validate a trading signal. If both the moving average and the RSI indicate to sell, the trader might conclude that the market sentiment is indeed bearish, prompting them to sell.
Caveats in Using Technical Indicators
While technical indicators are useful tools in market analysis and trading strategies, they are not a fail-safe mechanism. They are merely tools to analyze market behavior and predict potential trends based on past data. As markets are affected by a complex web of global economic, political, and societal factors, technical analysis cannot predict all market movements. Additionally, different indicators might sometimes provide conflicting signals, complicating decision-making. Therefore, they should be used as one part of a comprehensive trading strategy, augmenting decisions rather than driving them.
In summary, technical indicators are invaluable components in market research and analysis, granting traders significant insights into market trends, momentum, volatility, and volume. By using these indicators effectively, traders can elevate their decision-making and optimize their trading strategies. However, one must remember the inherent limitations of technical indicators and utilize them as a part of a broader, more profound understanding of the financial market.