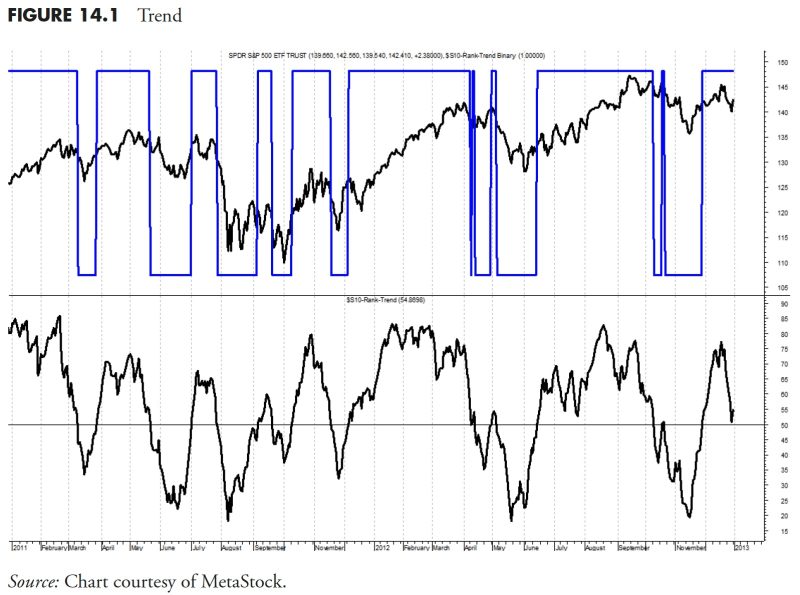
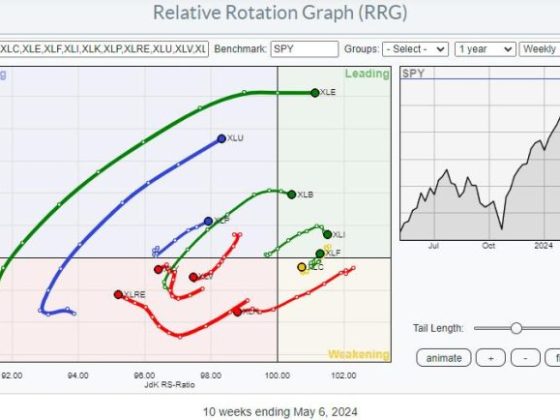
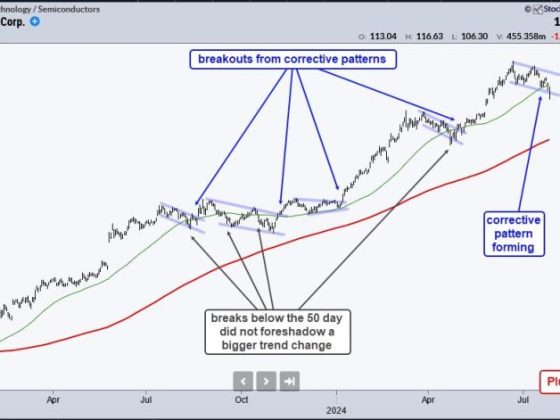
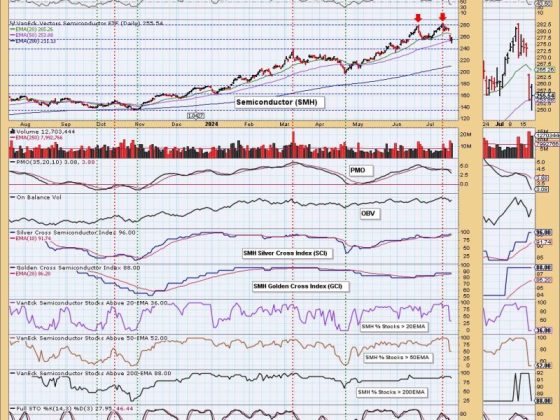
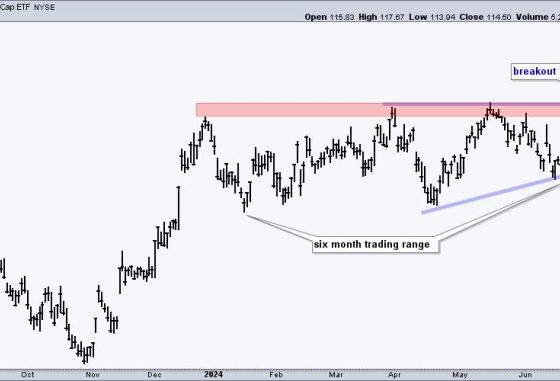
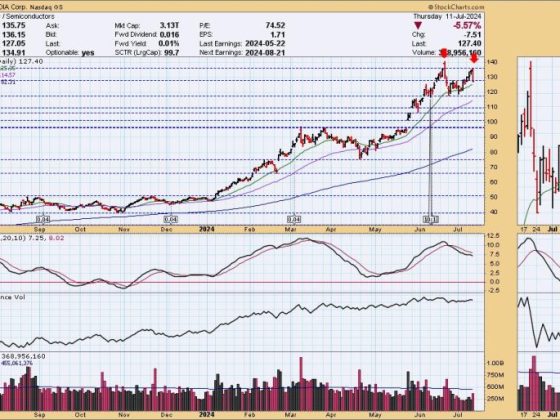
Every investor should aim for a steadfast financial course that aligns with their investment goals. In achieving this, rules-based money management plays a central role. One of the critical aspects of this strategy is the Security Ranking Measures. By effectively implementing these measures, one can significantly optimize their portfolio’s performance and thereby yield high returns. This part aims to unravel the essence of security ranking measures and illustrate their role in the realm of rules-based investing.
Rules-based money management, as we have elaborated in the previous parts of this series, is a systematic approach to investing that helps individuals make investment decisions based on predetermined guidelines. By taking emotions out of the equation, this strategy encourages investors to make rational, unfeigned, and profitable decisions. Security ranking measures form an integral part of these guidelines and exist as a set of parameters for judging the profitability of various securities.
There are different types of security ranking measures, and these range from relative strength measures, valuation measures, to fundamental measures.
1. Relative Strength Measures: This measure compares the performance of multiple securities with each other, establishing a rank by strength. The security demonstrating the highest return over a certain period receives the highest rank. An investor will lean more toward securities with high relative strength, implying superior momentum and performance.
2. Valuation Measures: These are used to evaluate a company’s worth to determine if a security is overpriced or underpriced. This includes measures like Price to Earnings (P/E) Ratio, Enterprise Value to EBITDA, and Price to Sales Ratio. Valuation measures facilitate decisions to buy, hold, or sell assets based on the determined relative value.
3. Fundamental Measures: Fundamental measures take into account the company’s financial health and growth prospects. These include factors like earnings per share, dividend yield, market capitalization, etc. Companies with robust fundamentals are usually considered solid investment options.
In implementing security ranking measures, investors can take two key approaches: the absolute scoring approach and relative scoring approach.
The absolute scoring approach ranks securities based on each measure independently. This means that one measure does not affect the ranking of another. A security’s final score is calculated as the average of the scores received in each category. Security with the highest average score is accorded the top rank. This approach is ideal for investors who regard each measure as equally important.
On the other hand, the relative scoring approach involves ranking securities based on overall scores in each category. The final score is the sum of the rankings in each measure. This approach accommodates investors who prioritize certain measures over others, allowing them to weigh the rankings according to their investment objectives.
In conclusion, security ranking measures are quintessential in rules-based money management. They provide a roadmap that guides investors in selecting profitable securities, while negating the influence of emotions and uninformed decisions. To fully harness the power of these measures, one must align them with their investment objectives and risk tolerance. This way, they can cruise towards their financial goals without unnecessary diversions.
Certainly, like any course of action, this system carries some inherent risks and is by no means foolproof. However, by continually updating the parameters involved and adjusting the scoring system according to evolving market dynamics, investors can significantly narrow down the margin of error. Therefore, a strategic approach to security ranking measures, tailored according to individual needs, is cardinal to successful rules-based money management.